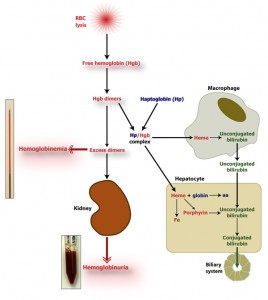
Intravascular hemolysis
The hemoglobin dimers that remain in circulation are oxidized to methemoglobin, which disassociates into a free heme and globin chains. The oxidized free heme (met-heme) binds to hemopexin (a β-globulin, Hpx) and the met-heme and hemopexin complex (met-heme/Hpx) is taken up by a receptor on hepatocytes and macrophages within the spleen, liver and bone marrow (only hepatocyte uptake is illustrated in the image above). Similarly, the hemoglobin/h…
Intravascular hemolysis Read More »