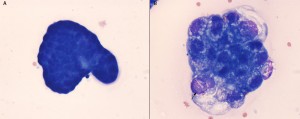
A. A cluster of “reactive” mesothelial cells in peritoneal fluid. These cells have central round nuclei with a moderate amount of medium to deep blue cytoplasm. Nuclear and cell features are uniform, arguing for a reactive versus neoplastic population.
B. Cluster of cells from a carcinoma in a peritoneal fluid from a cat. In contrast to the mesothelial cells in A, the cells show cytologic features of malignancy including moderate anisokaryosis and anisocytosis, variable nuclear to cytoplasmic ratios and prominent large oval nucleoli (arrow). They also have a coarse to ropey chromatin in contrast to the smoother chromatin of mesothelial cells. The cytoplasmic vacuolation is more commonly seen in carcinomas, but can be also be seen in mesothelial cells.